Trends in Employment and Earnings
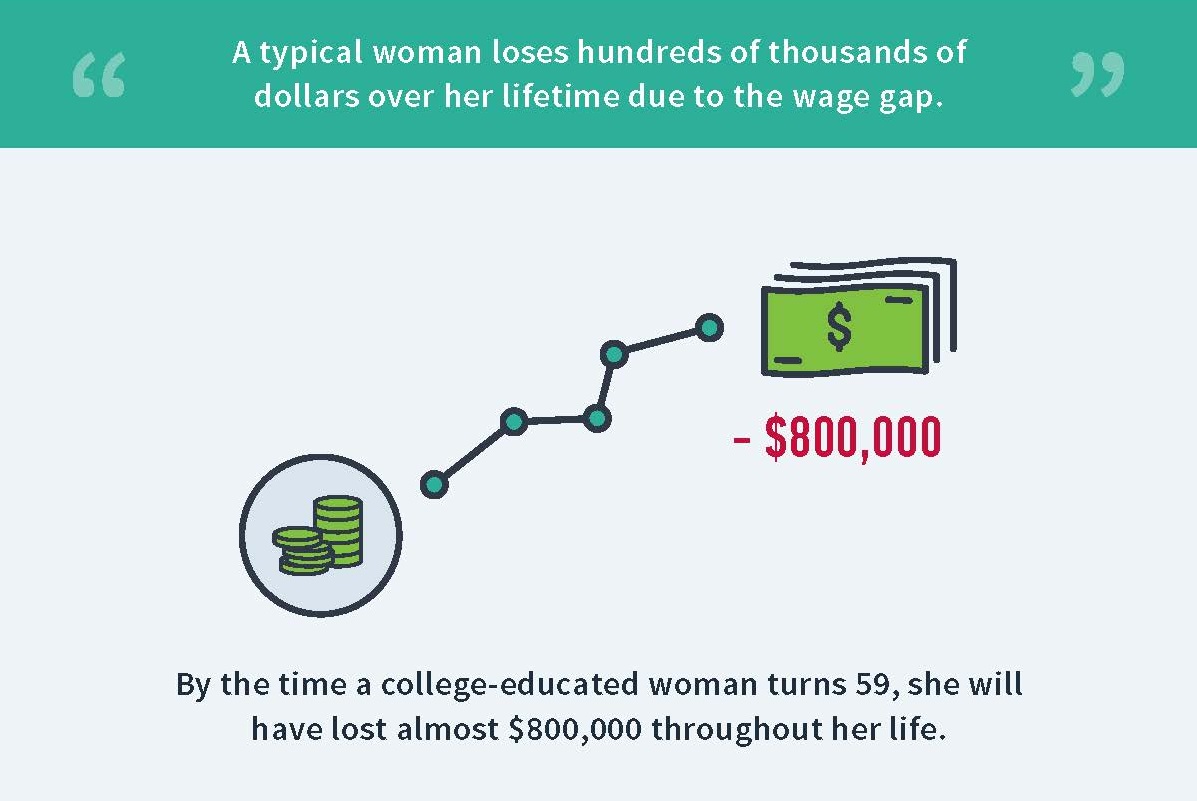
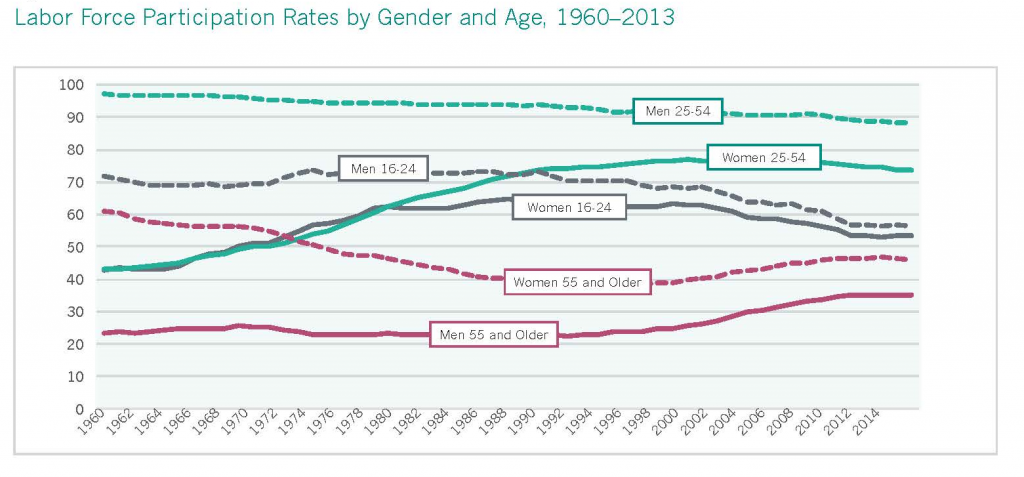
Women’s status in the area of employment and earnings has improved on two indicators since the publication of IWPR’s last national report on the status of women, the 2004 Status of Women in the States, and remained unchanged or declined on two others. Women’s median annual earnings for full-time, year-round work in 2013 ($39,157) were nearly identical to their earnings for similar work in 2002 ($39,108 when adjusted to 2013 dollars). The gender earnings ratio improved during this time from 76.6 to 78.3 percent, narrowing the gender wage gap by 1.7 percentage points, and the share of women working in professional or managerial occupations grew from 33.2 to 39.9 percent. Women’s labor force participation rate, however, declined from 59.6 in 2002 to 57.0 percent in 2014.
View All State Rankings See Key Indicators| Best | Worst |
|---|---|
| 1. District of Columbia | 51. Mississippi |
| 2. Maryland | 50. West Virginia |
| 3. Massachusetts | 49. Idaho |
| 4. Connecticut | 48. Louisiana |
| 5. New York | 47. Alabama |